Berdi
urinary Track Health
Do you know that the liver is the largest internal organ in your body? Even though it plays a critical role in keeping your body working efficiently. The liver fails to get its due recognition. Neglecting your liver health can lead you to get common liver issues like fatty liver disease. But what is fatty liver disease?
Fatty liver disease is a condition where too much fat accumulates in the liver, leading to inflammation and damage over time. It’s a surprisingly common condition. Fatty liver disease is the most common liver disease in industrialized and developed countries. It affects an estimated 25% of the global population.
There are two types of fatty liver disease: alcoholic and non-alcoholic. As the name suggests, alcoholic fatty liver disease is caused by excessive alcohol consumption. In contrast, non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is caused by factors like obesity, insulin resistance, and high cholesterol.
Alcoholic fatty liver disease (AFLD) is caused by excessive alcohol consumption. When you drink alcohol, your liver breaks it down into a substance called acetaldehyde, which can damage liver cells and lead to inflammation. Over time, this inflammation can cause scarring and permanent damage to the liver. AFLD can progress to more severe conditions such as alcoholic hepatitis and cirrhosis.
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), on the other hand, is caused by various factors, including obesity, insulin resistance, and high cholesterol. It’s the most common type of fatty liver disease, affecting an estimated 25% of the global population. NAFLD can range in severity from simple fatty liver, where there is only fat buildup in the liver, to non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), where there is inflammation and damage to liver cells.
Fatty liver disease symptoms can be vague, including fatigue, abdominal discomfort, and an enlarged liver. Some common symptoms of fatty liver disease are
Fatty liver disease is a condition that can affect anyone, but certain risk factors can increase the likelihood of developing the disease. Understanding these risk factors is important for prevention and early detection.
One of the main risk factors for fatty liver disease is obesity. People who are overweight or obese are more likely to develop fatty liver disease, as the excess fat in their bodies can be stored in the liver. In fact, studies have found that obesity is a major contributing factor to nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), the most common form of fatty liver disease.
Alcohol consumption is also a risk factor for fatty liver disease. While NAFLD is not caused by alcohol consumption, heavy drinking can cause alcoholic fatty liver disease (AFLD). This condition occurs when alcohol is processed by the liver and converted into fat, leading to inflammation and damage to the liver.
Genetics can also play a role in the development of fatty liver disease. Some people may be predisposed to the condition due to inherited genetic factors that affect how their body processes and stores fat.
Other risk factors for fatty liver disease include type 2 diabetes, high blood pressure, high cholesterol levels, and metabolic syndrome. These conditions can all contribute to the development of fatty liver disease by causing inflammation and damage to the liver over time.
Diagnosing fatty liver disease can be challenging, as many people with the condition do not experience any symptoms in the early stages. However, early diagnosis is important for preventing the disease from progressing and causing serious liver damage. There are several methods that doctors use to diagnose fatty liver disease.
One of the most common methods of diagnosing fatty liver disease is through imaging tests, such as an ultrasound, CT scan, or MRI. These tests allow doctors to visualize the liver and detect any signs of excess fat accumulation. An ultrasound is often the first imaging test that is done, as it is non-invasive and widely available.
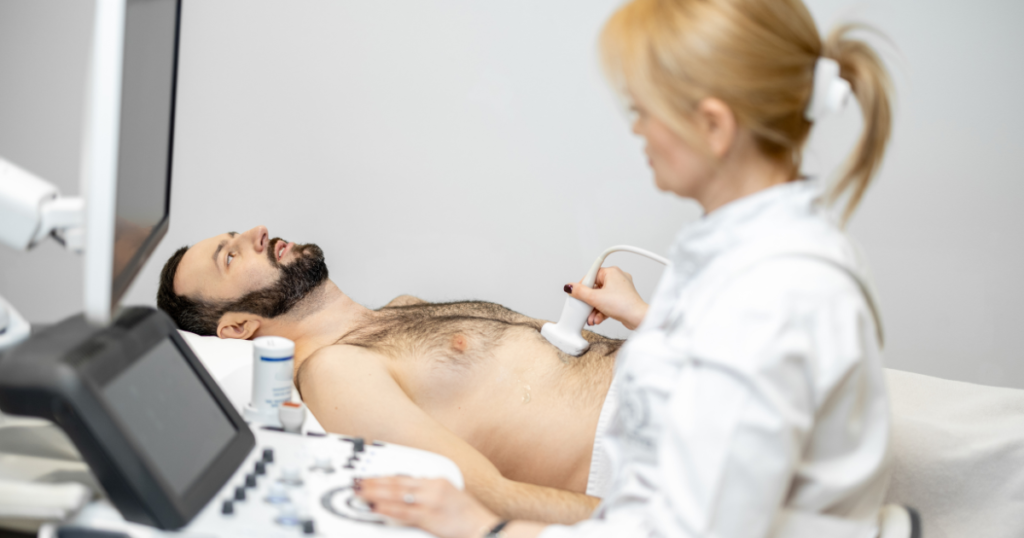
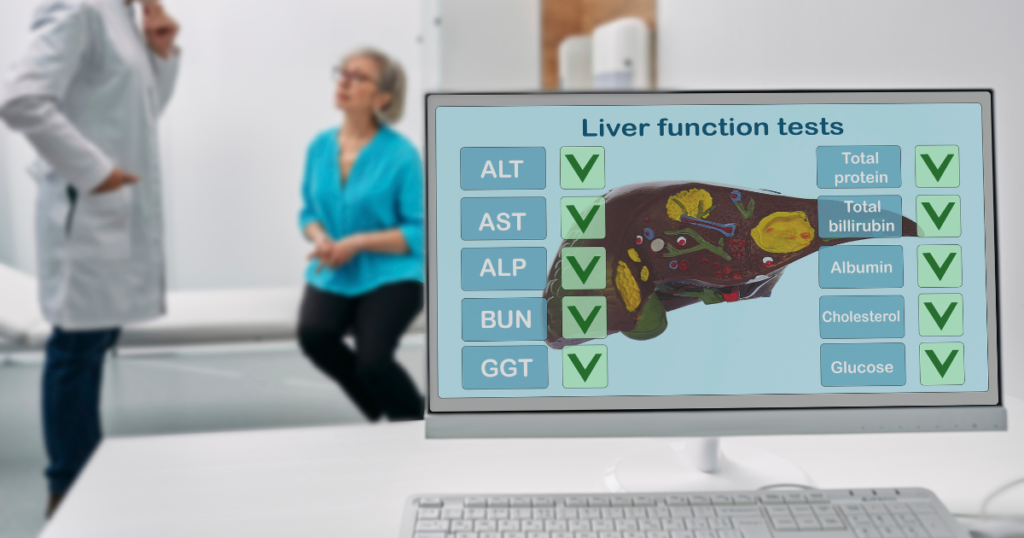
Blood tests can also be used to diagnose fatty liver disease. Elevated levels of liver enzymes, such as alanine aminotransferase (ALT) and aspartate aminotransferase (AST), can indicate liver inflammation and damage. However, it’s important to note that some people with fatty liver disease may have normal liver enzyme levels.
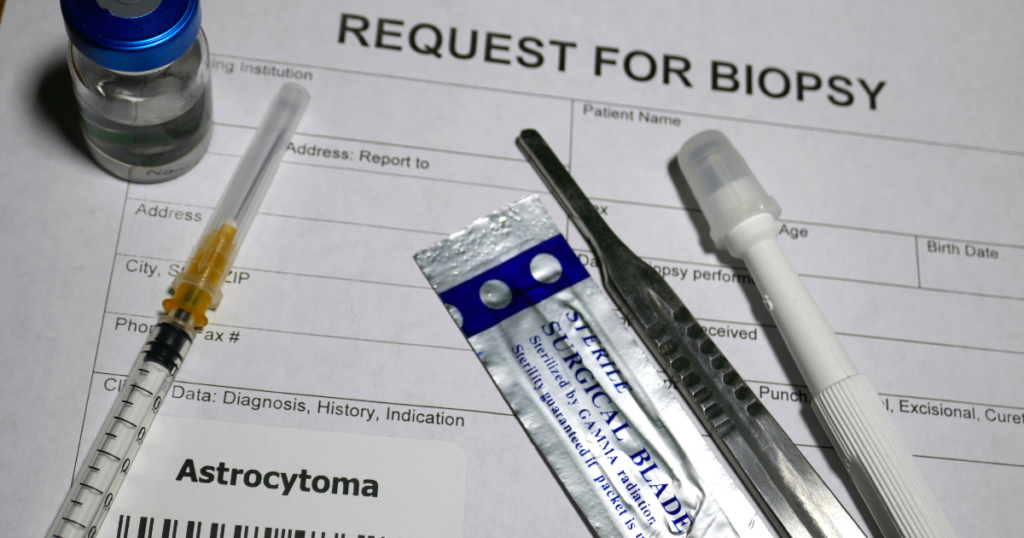
A liver biopsy is another method of diagnosing fatty liver disease. This involves taking a small sample of liver tissue and examining it under a microscope to look for signs of fat accumulation, inflammation, and liver damage. While liver biopsy is considered the gold standard for diagnosing fatty liver disease, it is an invasive procedure that carries some risks.
In some cases, a combination of these diagnostic methods may be used to confirm a diagnosis of fatty liver disease. It’s important to note that early detection and diagnosis of the condition is crucial for preventing further liver damage and complications.
There is a specific medication to treat fatty liver disease. Still, lifestyle changes and treatment of accompanying issues can help cure fatty liver.
Maintaining a healthy weight is one of the most important ways to manage fatty liver disease. Losing weight can help reduce the amount of fat in the liver and improve liver function. A weight loss of 5-10% of body weight is often recommended. This can be achieved through a combination of diet and exercise.
A healthy diet can help reduce the amount of fat in the liver and improve liver function. A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins is recommended while limiting or avoiding high-calorie, high-fat foods, sugary drinks, and alcohol. A low-carbohydrate diet may also be recommended.
Regular physical activity can help improve insulin sensitivity, which can help reduce the amount of fat in the liver. Exercise can also help with weight loss and improve overall health. The American Heart Association recommends at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity weekly exercise.
No specific medication can cure fatty liver disease, but some medications may be prescribed to manage related conditions or improve liver function. For example, medications may be prescribed to manage high blood pressure, high cholesterol, or diabetes. Vitamin E supplements may also be prescribed, as they have been shown to improve liver function in some cases.
If fatty liver disease is caused by an underlying condition, such as diabetes or high cholesterol, managing that condition is important for managing fatty liver disease. This may involve medications, lifestyle changes, or both.
A liver transplant may be necessary in severe cases of fatty liver disease. This involves replacing the damaged liver with a healthy liver from a donor. However, liver transplants are typically reserved for people with advanced liver disease who have not responded to other treatments.
It’s important to note that lifestyle changes, such as weight loss, diet changes, and exercise, are often the first line of treatment for fatty liver disease. Sometimes, these changes may be enough to improve liver function and prevent further liver damage. However, talking to your doctor about the best treatment plan for your needs is important.
Fatty liver disease can be prevented and managed by caring for your liver health. Products like Himalaya’s Liv.52 can help you take good care of your liver. Liv.52 is designed to treat and manage liver disorders like fatty liver, viral hepatitis, and liver damage. It also promises to help related issues like loss of appetite and protein energy malnutrition.
Lifestyle changes and appropriate medical care can help reduce fatty liver. Losing weight, avoiding alcohol, and exercising regularly can reduce fatty liver.
The early signs of fatty liver disease are unexplained weight loss, fatigue, and dull and aching pain on the top right of the tummy.
Fatty liver disease is not a serious complication. However, it can get serious if not treated on time.
Fatty liver disease can be reversed and cured if the patient reduces a substantial amount of weight and opts for recommended lifestyle changes.
Healthy foods like whole grains, fruits, and vegetables can help with fatty liver disease. More nuts and lean meat can also be beneficial.








©2023 Route2Health®️
NTN: 2229383
AN ASSOCIATED COMPANY OF HIGHNOON LABORATORIES
STRN: 0301999937728

WhatsApp us
