Berdi
urinary Track Health
Ah, the joys of the changing seasons! Whether it’s the chilly winter air or the rainy spring days, your body is susceptible to cold and flu year-round. You may be in the midst of a summer heatwave or basking in the fall, viruses can attack you anytime and anywhere. So, it’s important to know how to manage and treat these common illnesses whenever they strike. From sneezing fits to coughing spells, the symptoms of the common cold and flu can leave you feeling miserable and drained.
So, how can you best prepare for and cope with these pesky viruses? In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore everything you need to know about the causes, symptoms, and treatments of the common cold and flu, no matter what the season is.
The common cold and flu are both respiratory illnesses caused by viral infections, but there are some key differences between the two. The symptoms of the common cold are generally milder and more localized to the upper respiratory tract. Meanwhile, the flu can cause more severe symptoms and affect both the upper and lower respiratory tracts.
Some of the main differences between the common cold and flu include the onset and duration of symptoms, as well as the severity of those symptoms. According to The Journal of Clinical Virology, common cold symptoms typically develop over several days, while flu symptoms can develop more rapidly and may last for several weeks.
Additionally, the flu can be more dangerous than the common cold, especially for certain high-risk groups such as young children, older adults, and individuals with underlying health conditions. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) estimates that the flu has caused between 12,000 and 61,000 deaths annually in the United States alone since 2010.
The common cold and flu are both respiratory illnesses caused by viruses. The common cold is typically caused by the rhinovirus, while the flu is caused by influenza viruses. These viruses can spread through the air when an infected person coughs, sneezes, or talks and can also be spread through contact with infected surfaces.
According to research, over 200 strains of the rhinovirus cause the common cold, making it challenging to develop a vaccine. As for the flu, research has shown that there are several different types of influenza viruses, including influenza A, B, and C. Influenza A is known to cause more severe outbreaks and pandemics. In contrast, influenza B and C typically cause milder symptoms. Due to the many strains of viruses, it’s possible to get a cold or flu multiple times throughout your life, as your immune system may not recognize a new strain of the virus.
When a virus enters the body, it can invade the cells lining the nose, throat, and lungs. This triggers the immune system to respond, causing inflammation and an increase in mucus production. As a result, you may experience symptoms such as a runny or stuffy nose, coughing, sore throat, headaches, and body aches.
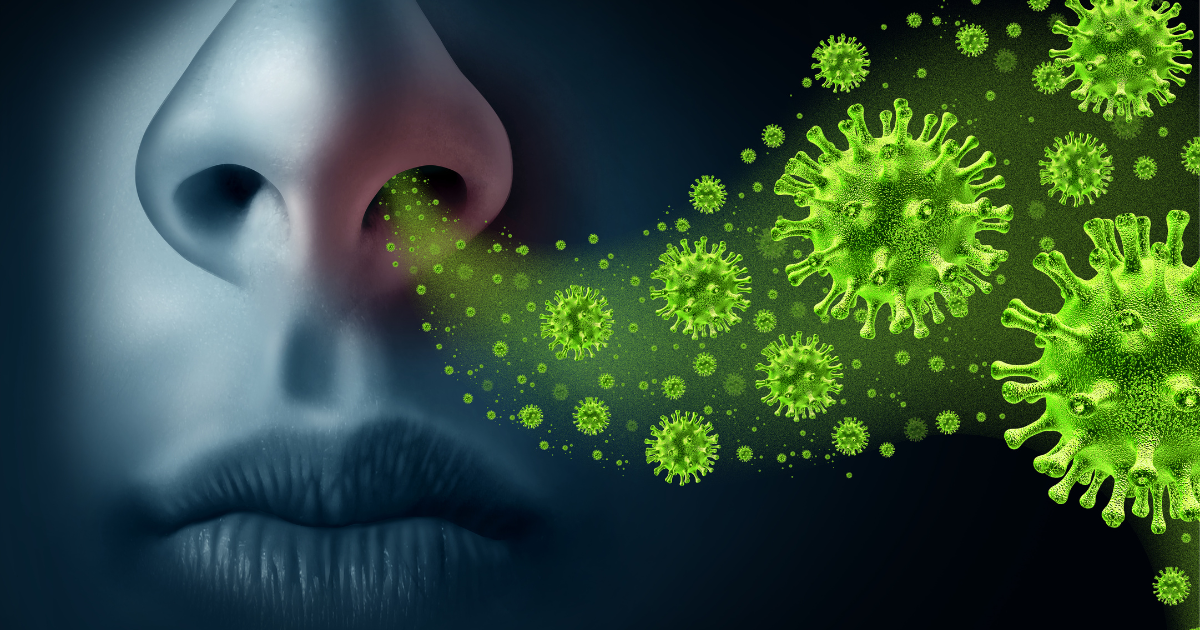
The symptoms of the common cold and flu can vary in severity and duration, but there are some key differences between the two illnesses. According to research, the common cold is usually characterized by symptoms localized to the upper respiratory tract, such as a runny or stuffy nose, sore throat, cough, and congestion. These symptoms typically develop gradually over a few days and may last for up to two weeks.
Conversely, the flu can cause more severe symptoms that affect both the upper and lower respiratory tracts. Flu can cause fever, body aches, fatigue, and sometimes even vomiting and diarrhoea. These symptoms can develop rapidly over a few hours and may last several weeks.
It’s important to note that not everyone with the flu will experience all of these symptoms, and some people may only experience mild symptoms. However, certain high-risk groups, such as young children, older adults, and individuals with underlying health conditions, may be more susceptible to developing severe flu symptoms.

There are certain risk factors that can increase your likelihood of developing a cold or the flu. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), some of these risk factors include
Even though certain factors can increase your risk of getting a cold and flu, certain precautionary measures can help you keep yourself safe.
Although cold and flu are not serious conditions and usually dont last for long, it is always better to take precautionary measures and avoid getting cold and flu.

There is no cure for the common cold or flu, but several treatments can help relieve symptoms and shorten the duration of the illness.
It’s important to note that antibiotics are not effective in treating colds or the flu, as these illnesses are caused by viruses rather than bacteria.
One of the most important treatment and prevention options for cold and flu is FluAce. FluAce is an enriching blend of plant roots and herbs that gives you fast and effective relief from flu and flu-like symptoms. This carefully curated herbal formula will help you get rid of nasal congestion, dry cough, chills, sweats, sore throat, fatigue, and weakness.
Most people recover from the common cold within 7-10 days, while the flu can last 1-2 weeks or longer.
Symptoms of a cold include a runny or stuffy nose, cough, sore throat, and mild fever. Symptoms of the flu are more severe and may include high fever, body aches, and fatigue.
To prevent colds and flu, it’s important to wash your hands frequently, avoid close contact with sick individuals, and get a flu vaccine every year.
No, antibiotics are not effective in treating viral infections like colds or the flu. They only work against bacterial infections.
You should see a doctor if your symptoms are severe or do not improve after a few days. Additionally, if you are at high risk for complications from the flu, such as young children, older adults, or those with certain health conditions, it’s important to seek medical attention.








©2023 Route2Health®️
NTN: 2229383
AN ASSOCIATED COMPANY OF HIGHNOON LABORATORIES
STRN: 0301999937728

WhatsApp us
