Berdi
urinary Track Health
In the intricate tapestry of the human body, our joints play a pivotal role in enabling movement and flexibility. Picture a well-oiled machine smoothly navigating the twists and turns of daily life. Now, imagine a disruption in this seamless operation—arthritis, a condition that affects millions worldwide, causing discomfort, pain, and a significant impact on the quality of life.
Arthritis, an umbrella term encompassing over 100 different types of joint-related conditions, is a widespread and often misunderstood health issue. From the elderly to the young, it doesn’t discriminate based on age, gender, or background. As we embark on this journey to understand arthritis, let’s peel back the layers of this multifaceted ailment, exploring its origins, symptoms, and the various forms it takes.
Understanding arthritis is crucial for early detection and effective management. It not only helps individuals recognise symptoms but also enables them to explore suitable treatment options, enhancing their overall well-being.
There are over 100 different types of arthritis, each with its own set of characteristics, symptoms, and underlying causes. However, some of the most common types include:
Osteoarthritis (OA): This is the most prevalent form of arthritis and is often associated with thageing. It occurs when the protective cartilage that cushions the ends of bones within a joint gradually wears down over time.
These are just a few examples, and the spectrum of arthritis is vast. Each type presents its own challenges, and proper diagnosis by a healthcare professional is essential for effective management and treatment. It’s crucial to note that early intervention and appropriate medical care can significantly improve the quality of life for individuals with arthritis.
Certainly, here are some common causes of arthritis presented in bullet points with proper sentences and relevant research references:
These causes contribute to the diverse spectrum of arthritis, and understanding arthritis and these factors is crucial for effective management and treatment. Individuals experiencing symptoms should consult healthcare professionals for accurate diagnosis and personalised care.
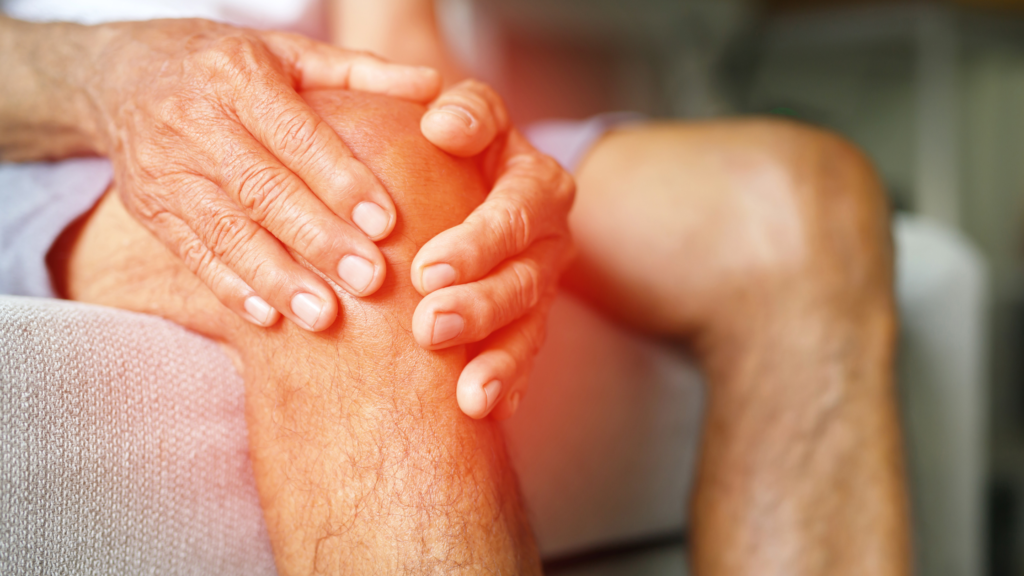

Understanding the symptoms of arthritis is as important as understanding arthritis. Here are the common symptoms associated with arthritis, presented in proper sentences:
These symptoms serve as general indicators, and it is crucial for individuals experiencing them to seek professional medical advice for accurate diagnosis and appropriate management.
After understanding arthritis and learning everything you need to know about it, it’s time to explore the common treatment options. Following are the common treatment options for arthritis. Keep in mind that the treatment depends on the type of arthritis and individual cases.
Pain relievers, anti-inflammatories, and disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) are commonly prescribed to manage symptoms.
Physical therapy aims to improve joint function and reduce pain through targeted exercises and stretches. The Physical Therapy & Rehabilitation Journal has given proper clinical practice guidelines for physical therapists for the management of rheumatoid arthritis.
Adopting a healthier lifestyle, including regular exercise and a balanced diet, can positively impact arthritis symptoms. Practices such as yoga and meditation can aid in stress reduction, benefiting arthritis patients. Some individuals find relief by adopting an anti-inflammatory diet and avoiding trigger foods. A study published in the journal “Best Practice & Research Clinical Rheumatology” shows that practices like regular exercise, losing weight, and changing footwear can improve symptoms of osteoarthritis.
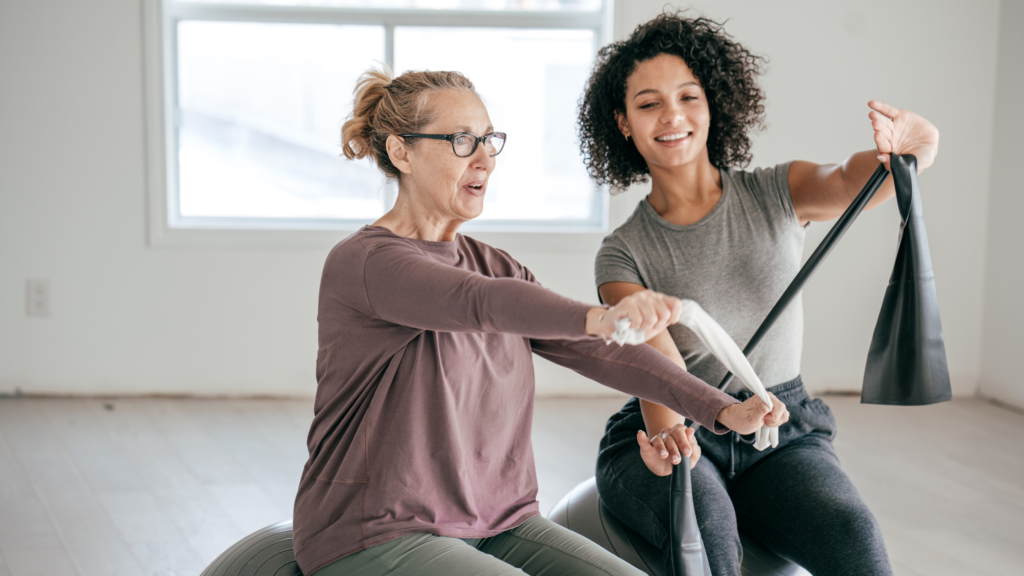

Surgery can be a viable treatment option for arthritis when conservative measures fail to alleviate symptoms. Procedures such as joint replacement surgery, arthroscopy, or joint fusion may be recommended to restore joint function and alleviate pain. While surgery is often reserved for severe cases, advancements in surgical techniques have improved outcomes, providing patients with an effective means to manage arthritis and improve their quality of life.
Alternative therapies like acupuncture and hijama work for many. Acupuncture, an ancient Chinese practice, involves inserting thin needles into specific points on the body to alleviate pain. In comparison, hijama or cupping involves the pricking of skin and sucking blood through a suction cup from certain spots. While there is not enough research to prove the efficacy of these therapies, people go for them for religious and cultural beliefs.

Certain herbs, like turmeric and ginger, have anti-inflammatory properties and may help manage arthritis symptoms. Another herb called Boswellia Serrata can significantly lessen inflammation and improve the symptoms of arthritis. Curcumin and Boswellia Serrata combined with vitamin D3 can do wonders for your joints. Route2Health’s Flexa Plus contains all three in the right quantities to support your joints. Just one tablet a day can help you significantly relieve arthritis symptoms.

Arthritis is typically a chronic condition, but effective management can significantly improve quality of life. A cure is rare, but symptom control is achievable.
Yes, some individuals find relief through natural remedies like herbal supplements, dietary changes, and alternative therapies.
Consulting a healthcare professional for a thorough diagnosis, including physical examination and relevant tests, is crucial to differentiate between types of arthritis.
A healthy, anti-inflammatory diet can contribute to managing arthritis symptoms and supporting overall joint health.
While arthritis is more common in older adults, certain types, like juvenile arthritis, can affect individuals of all ages.








©2023 Route2Health®️
NTN: 2229383
AN ASSOCIATED COMPANY OF HIGHNOON LABORATORIES
STRN: 0301999937728

WhatsApp us
