Berdi
urinary Track Health
Calcium, an essential mineral, stands as the cornerstone of overall health and well-being, playing a pivotal role in numerous physiological processes within the human body. Beyond its widely acknowledged contribution to the development and maintenance of strong bones and teeth, the role of calcium is to serve as a vital catalyst for a myriad of cellular functions. From muscle contraction and blood clotting to nerve transmission, this micronutrient operates as a silent orchestrator behind the scenes, ensuring the seamless execution of fundamental bodily tasks. However, despite the crucial role of calcium, its deficiency remains a prevalent concern globally, contributing to a range of health issues.
In this article, we delve into the multifaceted importance of calcium, exploring its impact on various aspects of human health and emphasising the necessity of incorporating this mineral into our daily dietary regimen.
Before understanding the role of calcium, it is crucial to learn some fundamentals.
Calcium is a mineral crucial for various bodily functions, including nerve transmission, muscle contraction, and blood clotting. It is the most abundant mineral in the body, primarily found in bones and teeth.
Calcium is essential for maintaining the integrity of our skeletal system and ensuring the proper functioning of muscles and nerves. It also contributes to heart health, blood clotting, and hormone regulation.
The recommended daily intake of calcium varies by age and gender. Adults typically need between 1000 to 1200 milligrams of calcium daily, with higher requirements during adolescence, pregnancy, and lactation.
According to the National Institute of Health, the RDA (Recommended Daily Allowance) of calcium is as follows.
| Age | Male | Female | Pregnant | Lactating |
| 0–6 months | 200 mg | 200 mg | ||
| 7–12 months | 260 mg | 260 mg | ||
| 1–3 years | 700 mg | 700 mg | ||
| 4–8 years | 1,000 mg | 1,000 mg | ||
| 9–13 years | 1,300 mg | 1,300 mg | ||
| 14–18 years | 1,300 mg | 1,300 mg | 1,300 mg | 1,300 mg |
| 19–50 years | 1,000 mg | 1,000 mg | 1,000 mg | 1,000 mg |
| 51–70 years | 1,000 mg | 1,200 mg | ||
| >70+ years | 1,200 mg | 1,200 mg |
The role of calcium is crucial in your body. Calcium plays the following essential roles in the human body.
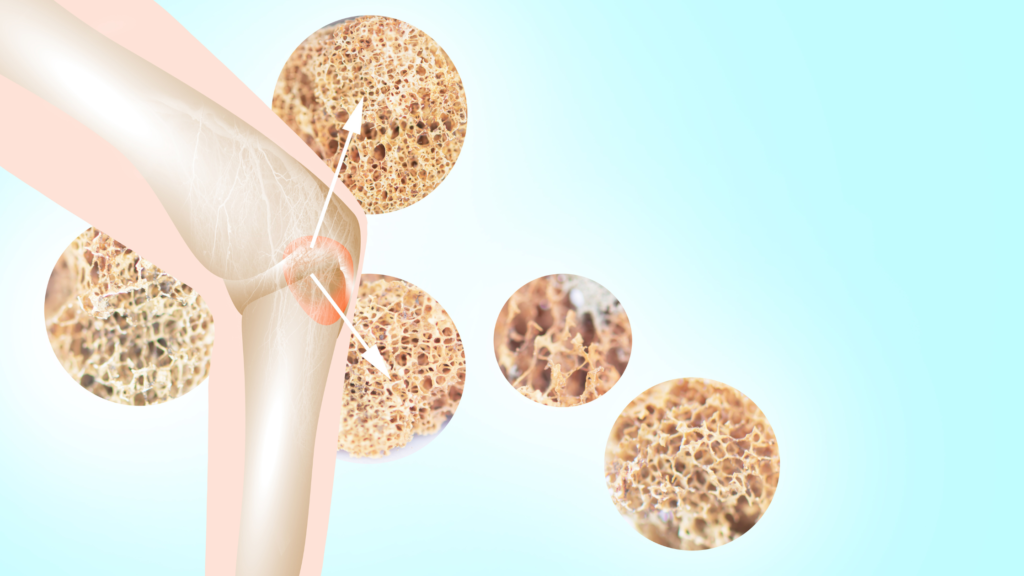
In the realm of human health, calcium emerges as a linchpin for the robustness and resilience of the skeletal system. Its pivotal role in bone health is multifaceted, impacting various aspects of bone development, maintenance, and overall strength.
Calcium comprises a substantial portion of the mineralised matrix that forms the structural foundation of bones. This mineral contributes to bone density and hardness, providing the necessary framework for the body’s architecture.
Numerous studies, including a meta-analysis in the British Medical Journal, have highlighted the positive correlation between dietary calcium intake and bone mineral density. Bone mineral density is a critical indicator of bone health, emphasising the need for adequate calcium to optimise bone mass and reduce the risk of conditions like osteoporosis.
Research yields compelling evidence supporting the role of calcium in reducing fracture risk. Postmenopausal women who receive calcium and vitamin D supplements exhibit a lower risk of hip fractures, underscoring the beneficial role of calcium supplementation in preserving bone integrity.
In conclusion, the significance of calcium in bone health extends far beyond the common perception of promoting strong bones. Scientific evidence emphasises the integral role of calcium in bone mineralisation, density, and overall skeletal well-being. As a fundamental mineral, calcium demands our attention and underscores the need for its inclusion in daily dietary practices to safeguard against bone-related issues and promote enduring skeletal strength.
Teeth, like bones, rely on calcium for strength and durability. Sufficient calcium intake contributes to healthy teeth, reducing the risk of decay and dental issues. Calcium plays a role in maintaining the integrity of tooth enamel, acting as a natural defence against acid erosion and decay. Including calcium-rich foods in the diet promotes good oral health.
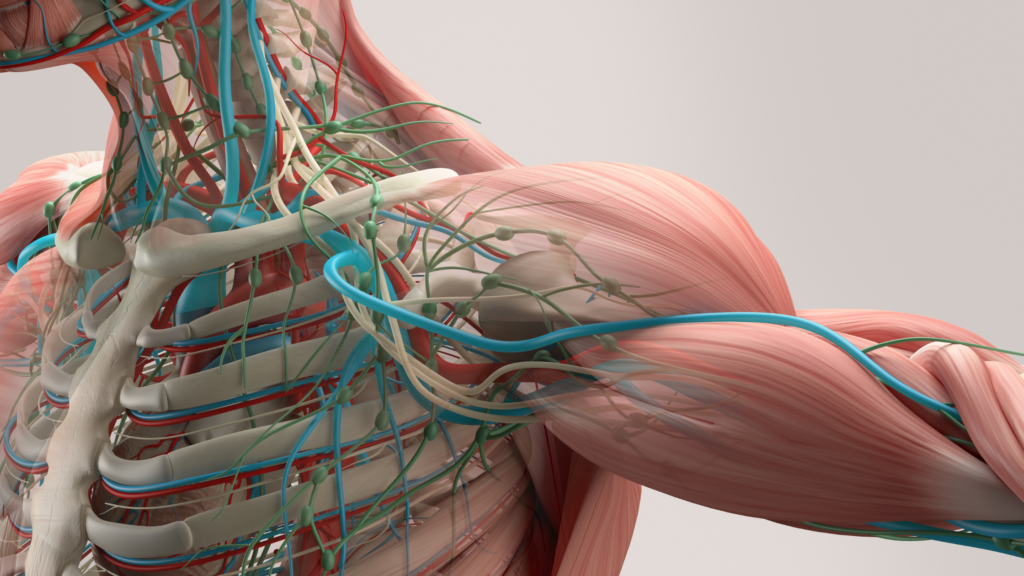
The role of calcium extends beyond bone health; it is an essential nutrient that ensures optimum muscle function, orchestrating vital processes that ensure the seamless operation of our musculoskeletal system.
The process of muscle contraction hinges on the interplay between calcium ions and proteins within muscle cells. As sarcomeres, the basic units of muscle contraction, shorten during muscle contraction, calcium ions are released from the sarcoplasmic reticulum, binding to troponin and initiating the complex series of events that lead to muscle contraction.
In a seminal study by Gordon et al. (2000), the molecular mechanisms underlying muscle contraction were dissected, underscoring the indispensable role of calcium in this process. The research highlights the interplay between calcium ions and contractile proteins, showing how disruptions in calcium regulation can compromise muscle function.
Beyond contraction, calcium is equally vital for muscle relaxation. The active transport of calcium ions back into the sarcoplasmic reticulum allows muscle fibres to relax, preparing them for subsequent contractions.
Calcium plays a crucial role in heart health, influencing various physiological processes, including muscle contraction, electrical conduction, and blood clotting. The heart, being a muscular organ, relies on calcium to facilitate the contraction and relaxation of its muscle cells, known as cardiomyocytes. Additionally, calcium is involved in the regulation of the heart’s electrical impulses, which coordinate the rhythmic beating of the heart.
Research studies have consistently highlighted the significance of calcium in maintaining heart health. Adequate calcium intake is associated with a reduced risk of cardiovascular events.
A meta-analysis examined the relationship between calcium supplementation and cardiovascular risk. The analysis, encompassing data from multiple randomised controlled trials, indicated that calcium supplementation did not significantly increase the risk of cardiovascular events. The study provided reassurance regarding the safety of calcium intake, supporting its role in maintaining heart health.
In terms of mechanisms, research explores the impact of calcium on vascular smooth muscle cells and vascular health. Invitro studies reveal that adequate levels of calcium contribute to the maintenance of vascular tone and endothelial function, both of which are critical for cardiovascular health.
In conclusion, research supports the crucial role of calcium in heart health. Adequate calcium intake and its influence on cardiovascular risk factors highlight the importance of this mineral in maintaining a healthy heart.

Calcium plays a crucial role in blood clotting, known as hemostasis. During clot formation, calcium acts as a cofactor in various enzymatic reactions, facilitating the conversion of prothrombin to thrombin, a key step in the clotting cascade. Research demonstrates the significance of calcium in platelet function and clot formation. Studies elucidate the calcium-dependent mechanisms involved in platelet aggregation, emphasising the essential role of calcium ions in the coagulation process.
Obtaining sufficient calcium from dietary sources is essential. Dairy products, leafy greens, nuts, and fortified foods are excellent choices. A diverse diet ensures a mix of nutrients, contributing to overall well-being.
For those with dietary restrictions or lactose intolerance, finding alternative sources of calcium is crucial. Supplements should be considered to get the optimum amount of calcium. High quality supplements like Bonical-K can give you enough amount of absorbable calcium to maintain optimum bone health, muscle function and heart health. Bonical-K also contains vitamin D3 and K1, ensuring stronger bones.

Recognising early signs of calcium deficiency, such as muscle cramps, numbness, and brittle nails, is essential for prompt intervention. Timely correction can prevent more severe complications.
Routine health check-ups should include assessments of calcium levels, especially for individuals with risk factors like poor dietary habits or medical conditions affecting calcium absorption.
Vitamin D and magnesium work in tandem with calcium. Ensuring an adequate intake of these nutrients supports overall bone health and optimises calcium utilisation in the body.
A holistic approach to nutrition involves considering the balance of various nutrients, including calcium. A diverse and well-rounded diet is key to achieving and maintaining optimal health.
In conclusion, calcium is not merely a component of strong bones but a cornerstone of overall health. From the foundation of our skeletal system to the intricacies of muscle function and hormonal balance, calcium’s influence is pervasive. By understanding its role and ensuring adequate intake through diet and, if necessary, supplements, individuals can pave the way for a healthier, more resilient life.
The recommended daily intake for adults varies but generally falls between 1000 to 1300 milligrams.
Symptoms include muscle cramps, numbness, brittle nails, and, in severe cases, osteoporosis.
Yes, calcium is found in various non-dairy sources like leafy greens, nuts, and fortified foods.
While supplements may be necessary in specific situations, obtaining calcium through a balanced diet is ideal.
Calcium plays a role in regulating hormones, contributing to stress response and blood pressure control.









©2023 Route2Health®️
NTN: 2229383
AN ASSOCIATED COMPANY OF HIGHNOON LABORATORIES
STRN: 0301999937728

WhatsApp us
